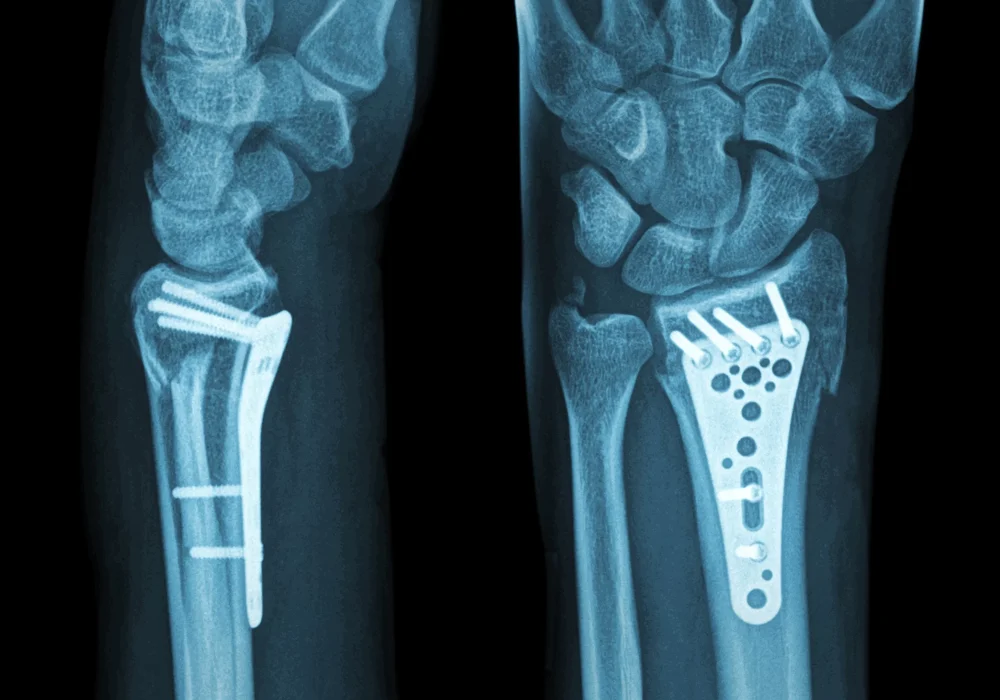
Distal radius plating
The distal radius is the end portion of the radius bone near the wrist joint. Fractures of the distal radius are among the most common orthopedic injuries, often resulting from falls onto an outstretched hand. These fractures can vary widely in severity, from simple, non-displaced breaks to complex, comminuted fractures involving the joint surface. Proper management is crucial to restore wrist function, prevent long-term complications, and ensure optimal patient outcomes.
What is Distal Radius Plating?
Distal radius plating is a surgical technique used to stabilize fractures of the distal radius using metal plates and screws. This method provides rigid fixation, allowing for early mobilization and improved anatomical alignment of the fractured bone fragments. The plates are typically made of stainless steel or titanium, designed to contour to the shape of the distal radius.
The goal of distal radius plating is to restore the normal anatomy of the wrist, maintain the length and alignment of the radius, and enable early wrist motion to reduce stiffness and improve functional recovery.
Indications for Distal Radius Plating
WRIST TREATMENTS
- Distal Radius Plating
- Percutaneous Scaphoid Screw
- Headless Screw Fixation of Carpus
- Dequervains Tenosynovitis Release
- Ganglion Cyst Removal
- Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
- Mini Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
- Open Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
- Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
- Scaphoid Nonunion Bone Grafting
- Scapholunate Ligament Reconstruction
- Proximal Row Carpectomy
- Arthroscopic TFCC Repair
- TFCC Reconstruction
- Limited Wrist Fusion Surgeries (SC fusion, RSL Fusion)
- Darrachs Procedure
- Wafers Resection of ulna
Make Your Appointment
Not all distal radius fractures require plating. The decision to perform plating depends on several factors, including:
- Fracture type and pattern: Intra-articular fractures, comminuted fractures, and fractures with significant displacement or instability often require plating.
- Patient factors: Age, bone quality, activity level, and comorbidities influence treatment choice.
- Failure of conservative treatment: If closed reduction and casting fail to maintain alignment, surgical fixation may be necessary.
- Open fractures: These often require surgical intervention to clean the wound and stabilize the fracture.
Types of Plates Used in Distal Radius Plating
Several types of plates are used depending on the fracture characteristics and surgeon preference:
1. Volar Locking Plates
Volar locking plates are the most commonly used implants for distal radius fractures. They are applied to the volar (palm) side of the radius and have locking screw technology that provides angular stability. This is especially beneficial in osteoporotic bone where screw purchase may be compromised.
2. Dorsal Plates
Dorsal plates are applied to the back of the wrist and are less commonly used due to higher rates of tendon irritation and rupture. They may be indicated in specific fracture patterns involving the dorsal aspect of the distal radius.
3. Fragment-Specific Fixation
In complex fractures, fragment-specific plates and screws may be used to stabilize individual bone fragments, allowing for precise anatomical reconstruction.
Surgical Technique
The surgical procedure for distal radius plating generally involves the following steps:
- Anesthesia and Positioning: The patient is placed supine with the arm on a hand table. Regional or general anesthesia is administered.
- Approach: The volar Henry approach is most commonly used, involving an incision along the volar aspect of the forearm to expose the distal radius.
- Fracture Reduction: The fracture fragments are carefully realigned under direct visualization and fluoroscopic guidance.
- Plate Application: The selected plate is contoured and positioned on the bone. Screws are inserted to secure the plate and maintain fracture reduction.
- Verification: Intraoperative imaging confirms proper alignment and hardware placement.
- Closure: The wound is closed in layers, and a sterile dressing is applied.
Postoperative Care and Rehabilitation
Postoperative management is critical to the success of distal radius plating:
- Immobilization: A splint or cast may be applied for a short period to protect the surgical site.
- Early Mobilization: Patients are encouraged to begin wrist and finger movements as soon as pain allows, usually within days after surgery.
- Physical Therapy: A structured rehabilitation program helps restore range of motion, strength, and function.
- Follow-up: Regular clinical and radiographic evaluations monitor healing and detect any complications early.
Advantages of Distal Radius Plating
- Stable fixation: Allows for early wrist motion, reducing stiffness.
- Anatomical restoration: Improves functional outcomes by restoring joint congruity.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of fracture patterns.
- Reduced need for prolonged casting: Minimizes complications related to immobilization.
Potential Complications
While distal radius plating is generally safe and effective, complications can occur:
- Infection: Superficial or deep infections may require antibiotics or hardware removal.
- Tendon irritation or rupture: Particularly with dorsal plates, extensor tendons may be affected.
- Nerve injury: The median nerve is at risk during volar approaches.
- Hardware problems: Screw loosening, plate breakage, or prominence causing discomfort.
- Malunion or nonunion: Improper healing leading to deformity or persistent pain.
Outcomes and Prognosis
Studies have shown that distal radius plating provides excellent functional outcomes, especially in younger patients and those with complex fractures. Most patients regain near-normal wrist motion and strength, allowing return to daily activities and work. Long-term complications such as post-traumatic arthritis are minimized with accurate anatomical reduction.
Innovations and Future Directions
Advances in implant design, such as low-profile plates and variable-angle locking screws, continue to improve outcomes. Minimally invasive surgical techniques and computer-assisted fracture reduction are emerging to reduce soft tissue damage and enhance precision.
Biodegradable plates and screws are also under investigation to eliminate the need for hardware removal. Additionally, 3D printing technology is being explored to create patient-specific implants tailored to individual anatomy.
Conclusion
Distal radius plating is a cornerstone in the surgical management of distal radius fractures, offering stable fixation and enabling early rehabilitation. Proper patient selection, meticulous surgical technique, and comprehensive postoperative care are essential to achieving optimal results. As technology advances, distal radius plating will continue to evolve, improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
