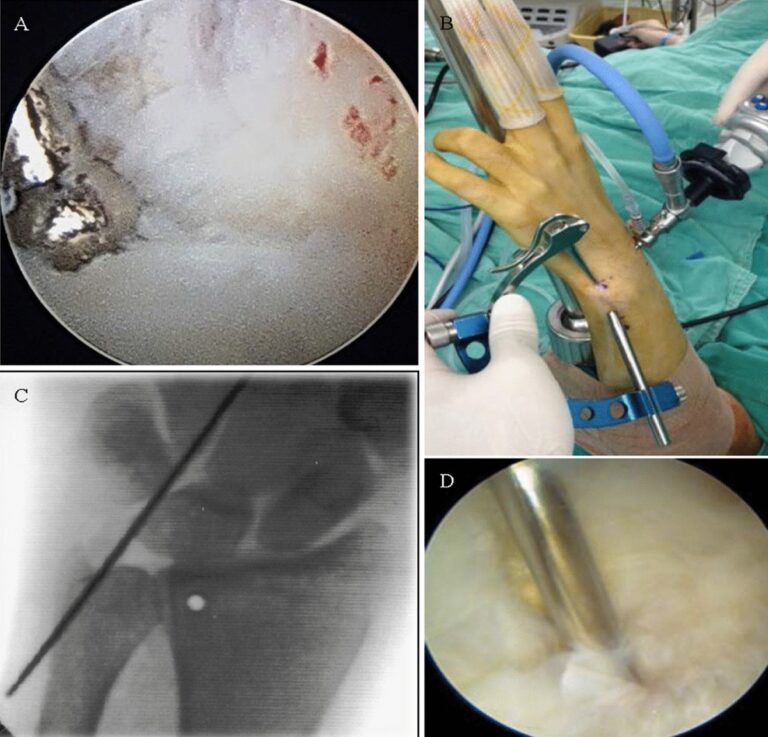
Arthroscopic TFCC Repair
The triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) is a critical structure in the wrist that provides stability and cushioning between the forearm bones and the small bones of the wrist. Injuries to the TFCC can cause significant pain, weakness, and loss of function in the wrist, impacting daily activities and quality of life. Arthroscopic TFCC repair is a minimally invasive surgical technique designed to restore the integrity of the TFCC, relieve pain, and improve wrist function.
This article provides an in-depth overview of the TFCC, common causes of injury, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and the arthroscopic repair procedure, including recovery and expected outcomes.
Understanding the TFCC
The TFCC is a complex structure composed of cartilage and ligaments located on the ulnar (little finger) side of the wrist. It acts as a stabilizer for the distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ) and supports the ulnar side of the wrist during rotational movements such as pronation and supination (turning the palm up and down).
WRIST TREATMENTS
- Distal Radius Plating
- Percutaneous Scaphoid Screw
- Headless Screw Fixation of Carpus
- Dequervains Tenosynovitis Release
- Ganglion Cyst Removal
- Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
- Mini Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
- Open Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
- Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
- Scaphoid Nonunion Bone Grafting
- Scapholunate Ligament Reconstruction
- Proximal Row Carpectomy
- Arthroscopic TFCC Repair
- TFCC Reconstruction
- Limited Wrist Fusion Surgeries (SC fusion, RSL Fusion)
- Darrachs Procedure
- Wafers Resection of ulna
Make Your Appointment
The TFCC consists of several components:
- The articular disc (triangular fibrocartilage)
- The meniscus homologue
- The ulnar collateral ligament
- The dorsal and volar radioulnar ligaments
- The sheath of the extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU) tendon
Together, these structures absorb compressive forces and stabilize the wrist during movement.
Causes of TFCC Injury
TFCC injuries can result from acute trauma or degenerative changes:
- Traumatic Injury: A fall onto an outstretched hand, especially with the wrist extended and twisted, can cause tears in the TFCC. Sports injuries, such as those sustained in gymnastics, racquet sports, or weightlifting, are common causes.
- Degenerative Tears: Repetitive stress, aging, and arthritis can lead to gradual wear and tear of the TFCC, resulting in degenerative tears.
- Ulnar Impaction Syndrome: When the ulna bone is longer than the radius (positive ulnar variance), it can cause increased pressure on the TFCC, leading to injury.
Symptoms of TFCC Injury
Patients with TFCC tears often experience:
- Ulnar-sided wrist pain, especially during gripping or twisting motions
- Swelling and tenderness on the ulnar side of the wrist
- Clicking or popping sensations during wrist movement
- Weakness or instability in the wrist
- Limited range of motion, particularly in rotation
Diagnosis
Diagnosing a TFCC injury involves a combination of clinical examination and imaging studies:
- Physical Examination: The doctor will assess wrist tenderness, range of motion, and perform specific tests such as the ulnar fovea sign, TFCC compression test, and piano key test.
- Imaging: X-rays are used to rule out fractures or bone abnormalities. MRI or MR arthrography provides detailed images of soft tissues and can identify TFCC tears.
- Arthroscopy: In some cases, wrist arthroscopy is both diagnostic and therapeutic, allowing direct visualization of the TFCC.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the severity and type of TFCC injury:
- Conservative Management: For minor or degenerative tears, rest, splinting, anti-inflammatory medications, and physical therapy may be sufficient.
- Steroid Injections: Corticosteroid injections can reduce inflammation and pain.
- Surgical Repair: When conservative treatment fails or in cases of significant tears, arthroscopic TFCC repair is recommended.
What is Arthroscopic TFCC Repair?
Arthroscopic TFCC repair is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that uses a small camera (arthroscope) and specialized instruments inserted through tiny incisions to repair the torn TFCC. This technique offers several advantages over open surgery, including less tissue damage, reduced pain, faster recovery, and smaller scars.
The Arthroscopic TFCC Repair Procedure
Preoperative Preparation
Before surgery, the patient undergoes a thorough evaluation, including imaging studies and medical clearance. The procedure is usually performed under regional or general anesthesia.
Surgical Steps
- Arthroscopic Access: Small incisions (portals) are made on the wrist to insert the arthroscope and surgical instruments.
- Inspection: The surgeon inspects the wrist joint, identifies the location and extent of the TFCC tear.
- Debridement: Damaged or frayed tissue is trimmed to create a healthy edge for repair.
- Repair: Depending on the tear type, the surgeon may use sutures, anchors, or other fixation devices to reattach the TFCC to the bone or surrounding ligaments.
- Assessment: The stability of the repair is tested arthroscopically.
- Closure: The instruments are removed, and the incisions are closed with sutures or steri-strips.
Duration and Hospital Stay
The procedure typically takes 30 to 90 minutes and is often performed on an outpatient basis, allowing the patient to go home the same day.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Immediate Postoperative Care
- The wrist is immobilized in a splint or cast for 4 to 6 weeks to protect the repair.
- Elevation and ice application help reduce swelling.
- Pain medications are prescribed as needed.
Physical Therapy
After immobilization, a structured rehabilitation program begins to restore wrist motion, strength, and function. Therapy includes:
Gentle range of motion exercises
Gradual strengthening exercises
Proprioceptive training to improve wrist stability
Return to Activities
Most patients can resume light activities within 6 to 8 weeks. Full return to sports or heavy manual work may take 3 to 6 months, depending on the injury severity and individual healing.
Benefits of Arthroscopic TFCC Repair
- Minimally Invasive: Smaller incisions reduce scarring and risk of infection.
- Faster Recovery: Less soft tissue disruption leads to quicker healing.
- Improved Outcomes: Direct visualization allows precise repair of the TFCC.
- Pain Relief: Effective reduction of ulnar-sided wrist pain.
- Restored Function: Enhanced wrist stability and strength.
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any surgery, arthroscopic TFCC repair carries some risks:
- Infection
- Nerve or blood vessel injury
- Stiffness or persistent pain
- Failure of the repair requiring revision surgery
However, these complications are relatively rare when performed by an experienced surgeon.
Conclusion
Arthroscopic TFCC repair is a highly effective surgical option for patients suffering from painful and unstable TFCC injuries. By restoring the integrity of this vital wrist structure, the procedure helps alleviate pain, improve wrist function, and enable patients to return to their daily activities and sports.
If you experience persistent ulnar-sided wrist pain or instability, consult a hand specialist or orthopedic surgeon to evaluate your condition. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment can prevent long-term complications and preserve wrist health.
