Joint Infections in Hand & Wrist (Septic Arthritis)
What is septic arthritis?
Septic arthritis (also known as infectious arthritis) happens when an infection spreads to one or more of your joints and causes inflammation. The inflammation is in the surface of the cartilage (a type of connective tissue) that lines your joints and the synovial fluid that lubricates your joints. Bacteria, a virus or fungus may cause the infection, which usually comes from another part of your body and spreads to your joint through your blood. Large joints such as your hip and knee are more commonly affected, but you could get septic arthritis in other joints such as your shoulder and ankle.
In the world of medicine, arthritis covers any type of joint inflammation. There are several different kinds of arthritis, including:
- Osteoarthritis.
- Rheumatoid arthritis.
- Psoriatic arthritis.
- Gout.
You might think that only older people get arthritis, but anyone at any age can get a type of arthritis. In fact, children more commonly experience septic arthritis than adults.
Which joints are more likely to have septic arthritis?
The joint that is most likely to be affected by septic arthritis depends on different factors. In general, larger joints in the lower half of your body, such as your hips, knees and ankles, are more commonly affected.
- Children are most likely to get septic arthritis in their hip.
- Adults are most likely to get septic arthritis in their knee.
- Injection drug users are more likely to get septic arthritis in the joints that connect your pelvis and lower spine (sacroiliac joints) and in the joint that connects your clavicle, or collarbone, to your sternum, or breastbone (sternoclavicular joint).
Can septic arthritis spread to other places in my body?
If the infection that caused your septic arthritis is not treated, the infection can spread to other parts of your body. This is called sepsis and is life-threatening.
Most cases of septic arthritis only involve one joint. In rare cases, multiple joints can have septic arthritis. Staphylococcal infections are the most common cause of septic arthritis, and most cases only involve one joint. Septic arthritis caused by Neisseria bacteria usually involves multiple joints.
HAND PROBLEMS
- Fractures and Dislocations in Hand
- Metacarpal & Phalangeal fractures
- Ligamentous injuries of fingers & Thumb
- Dislocations of finger joints
- Swellings of Fingers & Hand
- Compartment Syndrome
- Mucous cyst
- Ganglion cyst / Retinacular Cyst
- GCT of Tendon sheath
- Enchondroma (Benign Bone Tumor)
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Dupuytrens Contracture
- Post Traumatic Contracture
- Post Burn Contractures of fingers
- Volkmann Ischemic Contracture
- Stiff Fingers & CRPS
- Stiff joints of fingers and hand
- Osteoarthritis of Hand
- Finger joint arthritis
- Thumb Basal joint arthritis
- Acute Infections of Hand
- Finger Pulp Infection (Felon)
- Nail Fold Infection (Paronychia)
- Finger Infection (Flexor Tenosynovitis)
- Palm Infection (Deep Spaces of Hand infection)
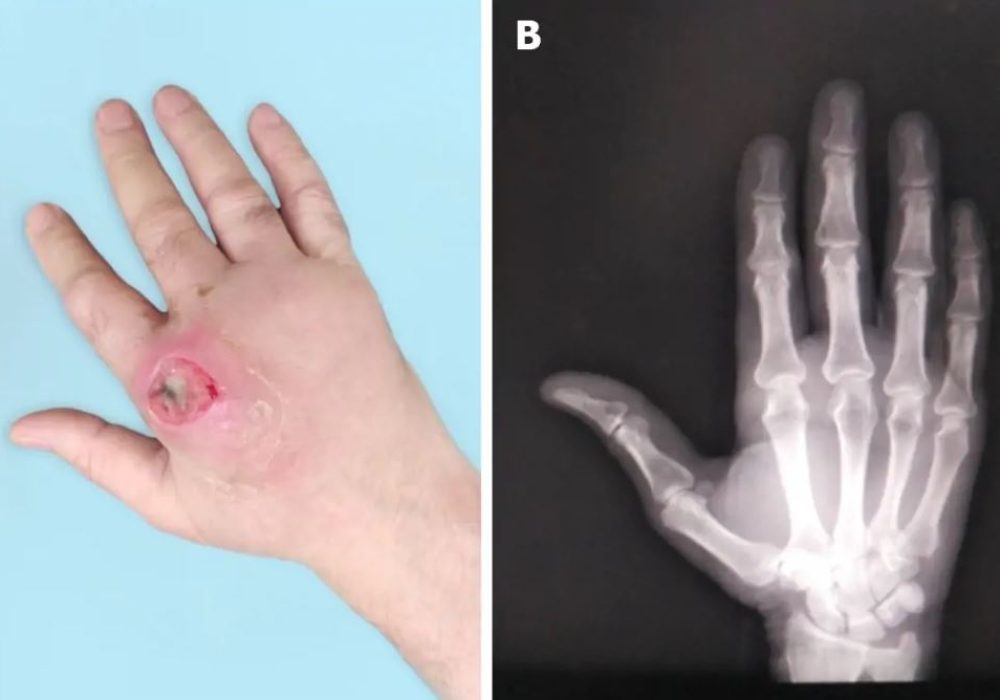
- Joint Infections in Hand & Wrist (Septic Arthritis)
- Human & Animal bite injuries to hand
- Diabetic Hand Infections
- Bacterial / Fungal / Atypical Hand infections in immunocompromised patients
- Subungual Hematoma
- Nail bed injury
- Nail Deformities
- Glomus tumor
Make Your Appointment
Who does septic arthritis affect?
Septic arthritis more commonly affects children, but adults can get it as well. People born male at birth between 2 and 3 years of age are most likely to get septic arthritis.
How common is septic arthritis?
Septic arthritis is not very common. There are approximately 2 to 6 cases of septic arthritis per 100,000 people per year.
How serious is septic arthritis?
Although it’s rare, septic arthritis is a serious condition. It can cause permanent damage to your affected joint and other complications. It can also cause death if it’s not treated. Be sure to see your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital immediately if you experience symptoms.
Symptoms and Causes
What are the symptoms of septic arthritis?
Symptoms of septic arthritis can include:
- Experiencing pain and tenderness in your affected joint.
- Having swelling and warmth at your affected joint.
- Having limited range of motion in your affected joint.
- Not wanting to use or move your affected joint.
- Having a fever.
What causes septic arthritis?
Septic arthritis is caused by an infection. It can be from bacteria, fungus, mycobacteria, a virus or other pathogens. In most cases, the infection begins somewhere else on or in your body and then spreads through your blood to your joint. More specifically, the following organisms can cause septic arthritis:
Staphylococcus aureus: This bacteria (also known as staph) is the most common cause of septic arthritis in both children and adults.
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA): MRSA is a type of staph infection that is resistant to some antibiotics. People who have a higher risk of getting septic arthritis from MRSA include those who use IV drugs, HIV (human immunodeficiency virus infection) or diabetes.
Groups A and B streptococci: Streptococci are a kind of bacteria. Elderly people and people with chronic diseases such as diabetes and cirrhosis are at higher risk of getting septic arthritis from streptococci.
Neisseria gonorrhoeae: This bacterium causes gonorrhea, a sexually transmitted infection (STI). People who have gonorrhea can get gonococcal arthritis, which is a form of septic arthritis.
Neisseria meningitides (meningococcus): This bacterium causes meningitis, which is a condition that involves inflammation (swelling) of the protective membranes covering your brain and spinal cord. While it can happen, getting septic arthritis from Neisseria meningitides is rare.
What is the most common bacteria that causes septic arthritis?
Staphylococcus aureus, a type of bacteria, is the most common cause of septic arthritis in both children and adults. Approximately 37% to 56% of septic arthritis cases are caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
Is septic arthritis contagious?
Septic arthritis is not contagious. However, the bacteria that cause septic arthritis, such as Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Neisseria gonorrhoeae, can spread from person-to-person contact.
Diagnosis and Tests
How is septic arthritis diagnosed?
After a physical exam of your joint, if your healthcare provider suspects you have septic arthritis, they will most likely withdraw synovial fluid (the fluid that lubricates your joint) from your affected joint with a needle. This is called aspiration. They will then do a laboratory test to look at the synovial fluid. Having bacteria in the synovial fluid of your joint confirms the diagnosis of septic arthritis.
What tests are used to diagnose septic arthritis?
Tests that are used to diagnose septic arthritis include:
- Synovial fluid aspiration: Your healthcare provider may withdraw fluid from your affected joint with a fine needle to check it for bacteria. This is known as aspiration.
- Blood tests: Your provider may have you undergo blood tests to see if your body’s immune system is responding to an infection and/or to rule out other possible issues.
- X-rays: X-rays use radiation to take images of your bones. X-rays can show widened joint spaces and bulging of the soft tissues, which can be signs of septic arthritis.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound uses sound waves to take pictures inside your body. An ultrasound can help your provider see how swollen your joint is and help them see your joint fluid when aspirating it.
- MRI: An MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) uses a large magnet, radio waves and a computer to make detailed images of your organs and bones. An MRI can help detect early cases of septic arthritis.
Management and Treatment
How is septic arthritis treated?
The following treatments are used for septic arthritis:
- Surgery: Removal of the inflamed tissue (surgical debridement) and IV (intravenous) antibiotics are necessary in most cases.
- Antibiotics: All cases of septic arthritis need to be treated with antibiotics. Your healthcare provider may give you antibiotics through an IV and/or in pill form.
- Joint fluid drainage: Your provider may drain (aspirate) fluid from your joint using a fine needle. They may have to do this more than once as you recover.
- Physical therapy: You will likely need physical therapy to restore function in your joint and prevent the muscles around your joint from weakening.
- Removal of an artificial joint: If you get septic arthritis in an artificial (prosthetic) joint, you will likely have to have your artificial joint removed and replaced with a joint spacer, a device made of antibiotic cement. After several months, your healthcare provider will replace your artificial joint.
How long does it take septic arthritis to heal?
The length of time it takes for septic arthritis to fully heal depends on what caused your infection and your overall health. You may have to take antibiotics for a few weeks. It could take longer for your joint to fully heal if the infection caused damage to your joint and the surrounding soft tissues.
Does septic arthritis go away on its own?
Septic arthritis cannot go away on its own since it’s an infection. Bacterial infections need to be treated with antibiotics. If you’re experiencing signs and symptoms of septic arthritis, contact your healthcare provider right away or go to the nearest hospital. Septic arthritis can lead to serious complications and can be life-threatening if it’s not treated.
