Chronic Hand Infections
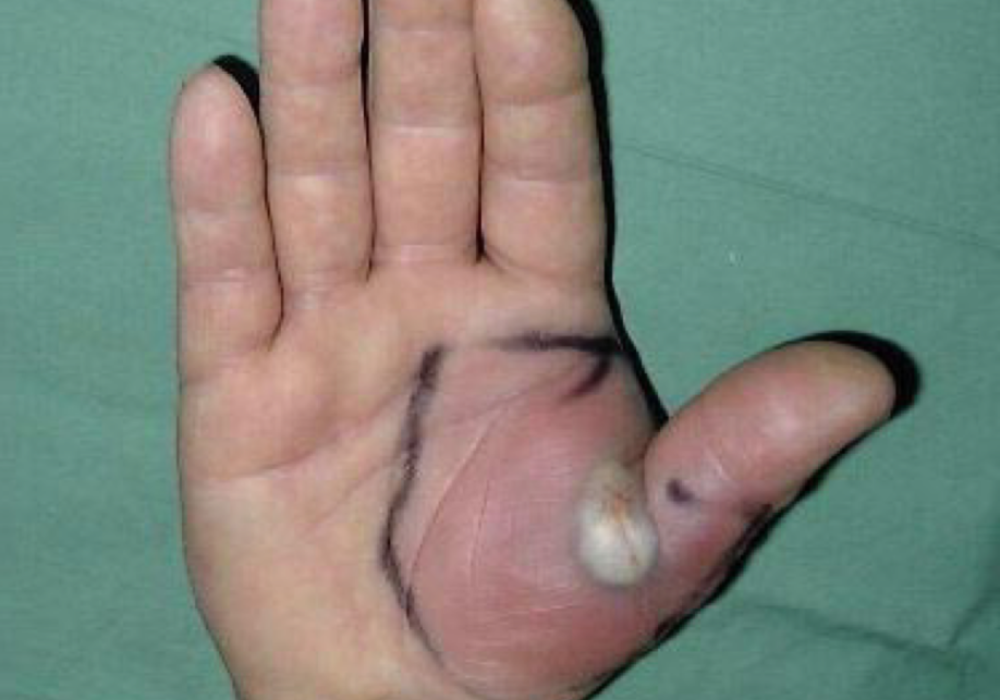
Chronic Hand Infections
Chronic hand infections are persistent infections that often involve deeper tissues such as bones, joints, or tendons and may be caused by bacteria, fungi, or mycobacteria. These infections can lead to long-term complications including stiffness, loss of function, and tissue damage if not properly diagnosed and treated. Management typically requires a combination of prolonged antibiotic or antifungal therapy, surgical intervention to drain abscesses or remove infected tissue, and rehabilitation to restore hand mobility and strength. Early recognition and aggressive treatment are essential to prevent permanent disability and improve outcomes.
Chronic Hand Infections: Overview
- Chronic hand infections are long-standing infections that often involve deep structures such as bones (osteomyelitis), joints (septic arthritis), tendon sheaths (tenosynovitis), or soft tissues.
- These infections may be caused by typical bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus, including MRSA, as well as atypical organisms such as mycobacteria (e.g., Mycobacterium marinum) and fungi (e.g., Candida albicans).
- They often develop insidiously and may be associated with delayed diagnosis or inadequate initial treatment of acute infections.
Causes and Risk Factors
- Direct inoculation from trauma, bites, or surgical procedures.
- Contiguous spread from superficial infections or wounds.
- Hematogenous spread, especially in immunocompromised patients.
- Repeated exposure to moisture or irritants, as seen in chronic paronychia.
- Immunosuppression, diabetes mellitus, intravenous drug use, and occupational hazards increase susceptibility.
Common Types of Chronic Hand Infections
- Chronic Paronychia: Persistent inflammation of the nail fold often caused by Candida species, especially in individuals with frequent water exposure.
- Osteomyelitis: Infection of the bone, commonly involving the distal phalanx, requiring prolonged antibiotic therapy and sometimes surgical debridement.
- Granulomatous Tenosynovitis: Often caused by atypical mycobacteria or fungi, presenting as chronic swelling and pain along tendon sheaths.
- Mycobacterial Infections: Including Mycobacterium marinum from aquatic injuries and Mycobacterium avium complex in immunocompromised hosts.
- Fungal Infections: Such as sporotrichosis following thorn injuries, and candidiasis in immunosuppressed patients.
HAND PROBLEMS
- Fractures and Dislocations in Hand
- Metacarpal & Phalangeal fractures
- Ligamentous injuries of fingers & Thumb
- Dislocations of finger joints
- Swellings of Fingers & Hand
- Compartment Syndrome
- Mucous cyst
- Ganglion cyst / Retinacular Cyst
- GCT of Tendon sheath
- Enchondroma (Benign Bone Tumor)
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Dupuytrens Contracture
- Post Traumatic Contracture
- Post Burn Contractures of fingers
- Volkmann Ischemic Contracture
- Stiff Fingers & CRPS
- Stiff joints of fingers and hand
- Osteoarthritis of Hand
- Finger joint arthritis
- Thumb Basal joint arthritis
- Acute Infections of Hand
- Finger Pulp Infection (Felon)
- Nail Fold Infection (Paronychia)
- Finger Infection (Flexor Tenosynovitis)
- Palm Infection (Deep Spaces of Hand infection)
- Joint Infections in Hand & Wrist (Septic Arthritis)
- Human & Animal bite injuries to hand
- Diabetic Hand Infections
- Bacterial / Fungal / Atypical Hand infections in immunocompromised patients
- Subungual Hematoma
- Nail bed injury
- Nail Deformities
- Glomus tumor
Make Your Appointment
Clinical Presentation
- Gradual onset of pain, swelling, erythema, and sometimes draining sinuses.
- Reduced range of motion and stiffness due to chronic inflammation and fibrosis.
- Possible systemic symptoms are usually mild or absent.
- Chronic infections may mimic other conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or gout.
Diagnosis
- Detailed history including occupational exposure, trauma, and immune status.
- Physical examination focusing on swelling, tenderness, and presence of sinus tracts.
- Laboratory tests: inflammatory markers (ESR, CRP), white blood cell count.
- Microbiological cultures from tissue biopsy or drainage to identify causative organisms.
- Imaging: X-rays may show bone changes; MRI or ultrasound can assess soft tissue involvement.
- Histopathology may be necessary for atypical infections.
Treatment
- Prolonged antimicrobial therapy tailored to the identified pathogen, often requiring weeks to months.
- Surgical intervention including drainage, debridement, or partial amputation may be necessary to remove infected tissue.
- Management of underlying conditions such as diabetes or immunosuppression is critical.
- Avoidance of predisposing factors, especially in chronic paronychia (e.g., moisture exposure).
- Adjunctive therapies include splinting, elevation, and hand therapy to preserve function.
Prognosis and Complications
- Early and appropriate treatment improves outcomes, but chronic infections can lead to permanent stiffness, deformity, and loss of function
- Delayed or inadequate treatment increases risk of complications such as tendon rupture, joint destruction, and systemic spread.
- Rehabilitation and close follow-up are essential to optimize recovery.
Patient Education and Prevention
- Educate patients on early signs of infection and importance of prompt medical evaluation.
- Advise on proper wound care and avoidance of repeated trauma or moisture exposure.
- Emphasize adherence to treatment regimens and follow-up appointments to prevent chronicity.
Challenges in Diagnosing Chronic Hand Infections
Chronic hand infections often present diagnostic challenges due to their subtle symptoms and slow progression. Unlike acute infections, patients may not exhibit classic signs such as high fever or marked redness. The infection may masquerade as other chronic inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or even tumors.
- Delayed Presentation: Patients may delay seeking care because symptoms are mild or intermittent.
- Atypical Organisms: Infections caused by atypical mycobacteria or fungi require specialized culture techniques and longer incubation periods.
- Imaging Limitations: Early bone or soft tissue changes may not be visible on plain X-rays; advanced imaging such as MRI or CT scans are often necessary.
- Need for Biopsy: Definitive diagnosis often requires tissue biopsy for histopathology and culture, especially in cases unresponsive to standard antibiotics.
Advanced Treatment Modalities
Management of chronic hand infections has evolved with advances in surgical techniques and antimicrobial therapy.
- Targeted Antimicrobial Therapy: Use of culture and sensitivity results to guide prolonged antibiotic or antifungal regimens, often lasting 6 weeks or more.
- Surgical Debridement: Removal of necrotic tissue and drainage of abscesses to reduce bacterial load and promote healing.
- Reconstructive Surgery: In cases with significant tissue loss, reconstructive procedures such as skin grafts, flaps, or tendon transfers may be necessary.
- Local Antibiotic Delivery: Use of antibiotic-impregnated beads or spacers in osteomyelitis to provide high local drug concentrations.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: Occasionally used as adjunctive treatment to enhance wound healing and combat anaerobic infections.
Rehabilitation and Functional Recovery
Restoring hand function after chronic infection is critical for patient quality of life.
- Physical Therapy: Early mobilization and exercises to prevent stiffness and maintain range of motion.
- Occupational Therapy: Focus on fine motor skills, grip strength, and activities of daily living.
- Splinting: Custom splints may be used to support healing tissues and prevent deformities.
- Pain Management: Addressing chronic pain through medications, nerve blocks, or other modalities.
- Psychosocial Support: Chronic hand infections can impact mental health; counseling and support groups may be beneficial.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing chronic hand infections involves both patient education and workplace safety.
- Proper Wound Care:Immediate cleaning and disinfection of hand injuries.
- Protective Equipment: Use of gloves and protective barriers in high-risk occupations.
- Avoidance of Moisture Exposure:Especially important in preventing chronic paronychia.
- Management of Comorbidities: Good control of diabetes and immune disorders reduces infection risk.
- Prompt Treatment: Early medical evaluation and treatment of acute hand infections to prevent chronicity.
Conclusion
Chronic hand infections are complex conditions that require a comprehensive approach for successful management. Early recognition, accurate diagnosis, appropriate antimicrobial therapy, surgical intervention when necessary, and dedicated rehabilitation are essential to restore hand function and prevent long-term disability. If you experience symptoms suggestive of a chronic hand infection, consult a healthcare professional promptly for evaluation and treatment.
