EPL Rupture
The Extensor Pollicis Longus (EPL) tendon plays a crucial role in thumb movement, enabling extension and allowing us to perform essential tasks such as gripping, pinching, and manipulating objects. An EPL rupture is a significant injury that can severely impair hand function and quality of life. This article provides a comprehensive overview of EPL rupture, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation.
What is the Extensor Pollicis Longus (EPL) Tendon?
The EPL tendon is part of the extensor muscle group in the forearm. It originates from the middle third of the ulna and the interosseous membrane and travels along the back of the wrist, passing through the third dorsal compartment of the wrist. It inserts at the base of the distal phalanx of the thumb.
The primary function of the EPL tendon is to extend the thumb at the interphalangeal joint, allowing the thumb to straighten out. This movement is essential for hand dexterity and performing fine motor tasks.
Tendon Problems
- Jersey Finger
- Zone II Flexor tendon injury
- Spaghetti Wrist
- Mallet Finger
- Swan neck Deformity
- Boutonniere Deformity
- Boxers Knuckle
- ECU Subluxation
- fight-bite-injury
- Extensor Tenosynovitis
- Flexor Tenosynovitis
- FCR Tendinitis
- FCU Tendinitis
- ECU tendinitis
- Calcific Tendinitis
- EPL Rupture
- Mannerfelt Syndrome
- Vaughan Jackson Syndrome
- Tendon Adhesions
Make Your Appointment
What is an EPL Rupture?
An EPL rupture refers to a complete tear or discontinuity of the extensor pollicis longus tendon. This injury results in the inability to extend the thumb fully, particularly at the distal joint. The rupture can be partial or complete, but complete ruptures are more disabling.
Causes of EPL Rupture
EPL ruptures can occur due to various reasons, including:
1. Trauma
Direct trauma to the wrist or thumb, such as a fall on an outstretched hand, can cause the EPL tendon to rupture. Fractures of the distal radius (Colles’ fracture) are commonly associated with EPL ruptures due to tendon attrition or direct injury.
2. Overuse and Repetitive Strain
Repetitive wrist and thumb movements, especially in athletes or workers performing repetitive tasks, can lead to tendon degeneration and eventual rupture.
3. Inflammatory Conditions
Conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis can cause inflammation around the tendon sheath, weakening the tendon and predisposing it to rupture.
4. Iatrogenic Causes
Surgical procedures around the wrist, such as distal radius fracture fixation, can inadvertently damage the EPL tendon.
5. Vascular Compromise
The EPL tendon has a relatively poor blood supply, especially around the Lister’s tubercle (a bony prominence on the distal radius). This makes it vulnerable to ischemic injury and spontaneous rupture.
Symptoms of EPL Rupture
The hallmark symptom of an EPL rupture is the inability to extend the thumb at the interphalangeal joint. Other symptoms include:
- Sudden onset of pain at the back of the wrist or thumb
- Swelling and tenderness over the dorsal wrist
- Weakness or loss of thumb function
- Difficulty performing tasks requiring thumb extension, such as releasing objects or typing
- A snapping or popping sensation at the time of injury (in some cases)
Diagnosis
Clinical Examination
A thorough physical examination is essential. The doctor will assess thumb extension by asking the patient to straighten the thumb against resistance. Inability to do so suggests an EPL rupture.
Imaging Studies
- X-rays: To rule out associated fractures, especially distal radius fractures.
- Ultrasound: Useful for visualizing tendon integrity and detecting ruptures.
- MRI: Provides detailed images of soft tissues and confirms the diagnosis, especially in partial tears.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the severity of the rupture, the time elapsed since injury, and the patient’s functional needs.
Non-Surgical Treatment
In cases of partial tears or when surgery is contraindicated, conservative management may be attempted. This includes:
- Immobilization with a thumb spica cast or splint for several weeks
- Anti-inflammatory medications to reduce pain and swelling
- Physical therapy to maintain range of motion and strength
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is the preferred treatment for complete EPL ruptures to restore thumb function. Surgical options include:
1. Primary Tendon Repair
If the rupture is diagnosed early (within a few weeks), direct end-to-end repair of the tendon may be possible.
2. Tendon Grafting
In cases where the tendon ends cannot be approximated due to retraction or degeneration, a tendon graft (using a tendon from another part of the body) may be necessary.
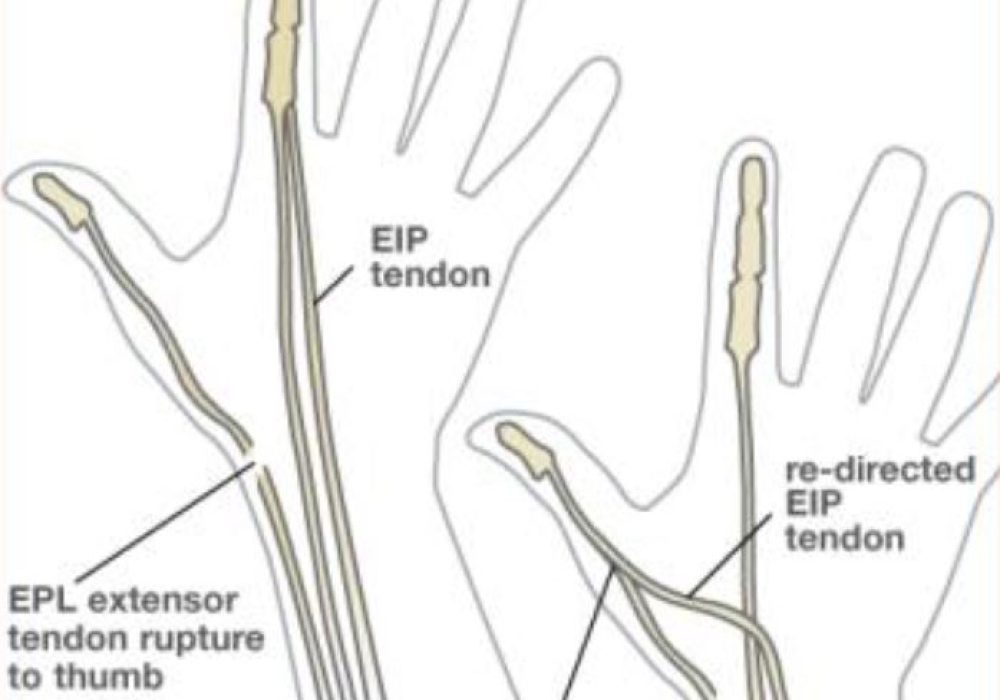
3. Tendon Transfer
A common surgical technique involves transferring the Extensor Indicis Proprius (EIP) tendon to replace the ruptured EPL tendon. The EIP tendon is harvested and rerouted to restore thumb extension. This procedure has excellent functional outcomes.
Rehabilitation
Postoperative rehabilitation is critical for optimal recovery. It typically involves:
- Immobilization in a thumb spica cast or splint for 4-6 weeks to protect the repair
- Gradual introduction of passive and active range of motion exercises under the guidance of a hand therapist
- Strengthening exercises to restore grip and pinch strength
- Functional training to regain fine motor skills
Full recovery may take several months, but most patients regain good thumb function.
Complications
Potential complications of EPL rupture and its treatment include:
- Stiffness and reduced range of motion
- Tendon adhesions or scarring
- Re-rupture of the tendon
- Infection (post-surgical)
- Donor site morbidity (in tendon transfer procedures)
Prevention
While some EPL ruptures are unavoidable, certain measures can reduce risk:
- Use protective gear during sports and high-risk activities
- Avoid repetitive strain by taking breaks and using ergonomic tools
- Early treatment of wrist fractures and inflammatory conditions
- Proper surgical technique during wrist surgeries
Conclusion
EPL rupture is a debilitating injury that affects thumb extension and hand function. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, often surgical, are essential to restore thumb mobility and strength. With advances in surgical techniques and rehabilitation protocols, most patients achieve excellent outcomes. If you experience sudden loss of thumb extension or wrist pain after injury, seek prompt medical evaluation to prevent long-term disability.
