Biceps Rupture
The biceps muscle, located in the front part of the upper arm, plays a crucial role in the movement and function of the arm. It is responsible for flexing the elbow and rotating the forearm. A biceps rupture refers to a tear or complete rupture of the biceps tendon, which connects the biceps muscle to the bones of the shoulder or elbow. This injury can significantly impact arm strength and function, making it essential to understand its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
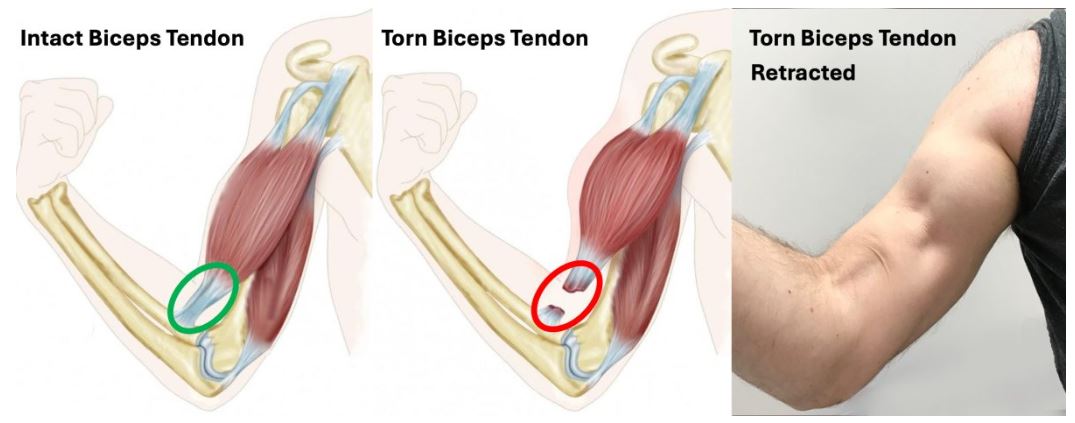
Anatomy of the Biceps Tendon
The biceps muscle has two tendons at its upper end: the long head and the short head. These tendons attach the muscle to the shoulder. At the lower end, a single tendon attaches the biceps muscle to the radius bone near the elbow. A rupture can occur at either the proximal (shoulder) or distal (elbow) tendon, with proximal ruptures being more common.
Causes of Biceps Rupture
Biceps ruptures typically occur due to sudden injury or chronic wear and tear. Common causes include:
Elbow Problems
Make Your Appointment
- Trauma or sudden injury:A sudden forceful movement, such as lifting a heavy object or falling on an outstretched arm, can cause the tendon to tear.
- Overuse and repetitive stress:Overuse and repetitive stress:
- Degeneration: Tendons can weaken with age due to decreased blood supply and microtears, making them more susceptible to rupture.
- Steroid use: Both systemic and local steroid injections can weaken tendons.
- Other risk factors: Smoking, certain medical conditions like diabetes, and previous tendon injuries can increase the risk.
Types of Biceps Rupture
- Proximal biceps rupture:This involves the tendon near the shoulder. It is more common and often occurs in older adults with degenerative tendon changes.
- Distal biceps rupture: This involves the tendon near the elbow and is less common but usually results from a sudden injury in younger, active individuals.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing a biceps rupture involves a combination of clinical examination and imaging studies:
- Physical examination: A healthcare provider will assess the arm for deformity, tenderness, and strength. Specific tests, such as the “hook test” for distal ruptures, may be performed.
- Imaging:
- X-rays can rule out fractures.
- Ultrasound is useful for visualizing tendon tears.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) provides detailed images of soft tissues and is the gold standard for confirming the extent and location of the rupture.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the type of rupture, patient age, activity level, and functional demands.
Non-Surgical Treatment
Non-surgical management may be appropriate for:
- Older patients with low functional demands.
- Partial tears.
- Proximal ruptures where the short head remains intact.
Non-surgical treatment includes:
- Rest and activity modification: Avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms.
- Ice and anti-inflammatory medications: To reduce pain and swelling.
- Physical therapy: To maintain range of motion and strengthen surrounding muscles.
- Bracing or splinting: In some cases, to support the arm during healing.
While non-surgical treatment can relieve pain and restore some function, it may result in decreased strength, especially in supination (rotating the forearm).
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is often recommended for:
- Distal biceps ruptures.
- Active individuals who require full strength and function.
- Complete proximal ruptures in younger patients.
Surgical repair involves reattaching the torn tendon to the bone. Techniques vary but generally include:
- Single or double incision approaches for distal repairs.
- Arthroscopic or open repair for proximal ruptures.
Post-surgery, patients undergo a period of immobilization followed by physical therapy to restore motion and strength.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery time depends on the severity of the rupture and treatment method. Generally:
- Non-surgical recovery may take several weeks to months, with gradual return to activities.
- Post-surgical recovery involves immobilization for 2-6 weeks, followed by progressive physical therapy. Full recovery can take 3-6 months.
Rehabilitation focuses on:
Focused Rehabilitation and Recovery
- Restoring range of motion.
- Strengthening the biceps and surrounding muscles.
- Gradual return to functional and sports activities.
Complications
Potential complications of biceps rupture and its treatment include:
- Persistent weakness or loss of strength.
- Stiffness or decreased range of motion.
- Re-rupture of the tendon.
- Nerve injury during surgery.
- Infection (rare).
Prevention
Preventing biceps rupture involves:
- Avoiding sudden heavy lifting or jerking motions.
- Gradual conditioning and strengthening of the arm muscles.
- Proper warm-up before physical activity.
- Avoiding smoking and managing medical conditions that affect tendon health.
- Using proper technique during sports and lifting.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience sudden pain, swelling, or weakness in your upper arm or elbow, especially after an injury, seek medical evaluation promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve outcomes and reduce complications.
Conclution
A biceps rupture is a significant injury that affects the tendons connecting the biceps muscle to the shoulder or elbow. It can result from trauma, overuse, or degeneration and presents with pain, weakness, and deformity. Diagnosis involves clinical examination and imaging, while treatment ranges from conservative management to surgical repair depending on the injury type and patient needs. With appropriate care and rehabilitation, most individuals can regain good arm function and strength.
