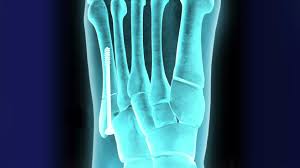
Fracture Fixation
Fracture fixation is a medical procedure aimed at stabilizing broken bones, ensuring proper alignment, and creating an optimal environment for healing. When a bone breaks, it loses continuity and stability, which can impair movement, cause pain, and lead to functional disability if not treated correctly. Fixation provides mechanical stability to the fractured site, preventing abnormal motion, reducing pain, and allowing the bone to heal in its correct anatomical position.
This method is an essential part of modern orthopedic surgery and can involve both non-surgical (external support) and surgical (internal or external devices) approaches. The choice of fixation depends on factors such as the type of fracture, bone involved, patient’s age, activity level, and overall health.
Understanding Fracture Fixation
Fracture fixation involves stabilizing broken bones using medical implants like plates, screws, wires, or specialized external devices. The goal is to hold the bones securely in the correct position while they heal, preventing deformity and preserving natural hand movement.
Common scenarios include:
Hand Treatments
Make Your Appointment
- Thorough clinical examination to assess swelling, alignment, and soft tissue health
- High‑resolution X‑rays or CT scans to analyze fracture complexity
- Discussion of patient occupation, lifestyle, and functional expectations
- Planning for potential combined procedures, such as tendon or nerve repair in severe trauma cases
Objectives of Fracture Fixation
- Anatomical Reduction – Restoring the broken bone fragments to their normal alignment.
- Stability – Providing mechanical support to prevent movement at the fracture site.
- Early Mobilization – Allowing early movement of the joints around the fracture to avoid stiffness, muscle wasting, and complications like deep vein thrombosis.
- Optimal Healing – Promoting biological conditions that allow bone regeneration and remodeling.
- Restoration of Function – Ensuring that the patient regains as much pre-injury function as possible.
Advanced Techniques and Expert Care
Modern fracture fixation relies on minimally invasive methods whenever possible, using specially designed implants suited for small hand and wrist bones. At our center, we focus on:
- Preserving blood supply to the bone and surrounding tissues for faster healing
- Achieving stable fixation to allow early, gentle movement
- Using low‑profile plates to reduce discomfort and risk of tendon irritation
- Combining fixation with soft tissue reconstruction when required
Biological Considerations in Fixation
Fracture healing occurs through two main processes:
- Primary (Direct) Healing – Seen in rigidly fixed fractures where bone heals directly without forming a callus.
- Secondary (Indirect) Healing – Occurs in less rigid fixation, where callus forms and gradually remodels into normal bone.
Surgeons must balance mechanical stability with biological healing capacity. Too rigid fixation may impair healing, while too little stability leads to delayed union or non-union.
Indications for Surgical Fixation
- Fracture is displaced and cannot be reduced by closed methods.
- Open fractures (bone exposed through skin).
- Multiple fractures or polytrauma cases.
- Fractures with associated vascular or nerve injuries.
- Pathological fractures (caused by bone weakness due to disease).
- Non-union or malunion of previously treated fractures.
Complications of Fracture Fixation
- Infection (more common in open fractures and external fixators).
- Implant failure such as breakage or loosening of screws and plates.
- Delayed Union or Non-Union, where healing is impaired.
- Malunion, where bones heal in the wrong position.
- Joint Stiffness or Muscle Atrophy due to prolonged immobilization.
- Neurovascular Injury during surgery.
Advances in Fracture Fixation
- Biodegradable Implants: Materials that dissolve over time, eliminating the need for implant removal surgery.
- Locked Plating Systems: Provide superior fixation in osteoporotic or comminuted fractures.
- Computer-Assisted Surgery and Navigation Systems: Increase accuracy of implant placement.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: Smaller incisions reduce soft tissue damage and promote faster recovery.
Rehabilitation After Fixation
Rehabilitation is as important as the fixation itself. Early mobilization of joints, guided physiotherapy, weight-bearing as tolerated, and strengthening exercises help restore normal function. The rehabilitation plan depends on fracture type, fixation method, and patient’s overall condition.
Conclusion
Fracture fixation is a cornerstone of modern trauma and orthopedic care. It restores stability, allows bones to heal properly, and helps patients regain normal function. From simple casts to advanced surgical implants, the methods of fixation have evolved greatly, improving recovery outcomes and reducing disability. However, careful patient assessment, appropriate choice of fixation technique, and proper rehabilitation are essential to achieve successful results.
