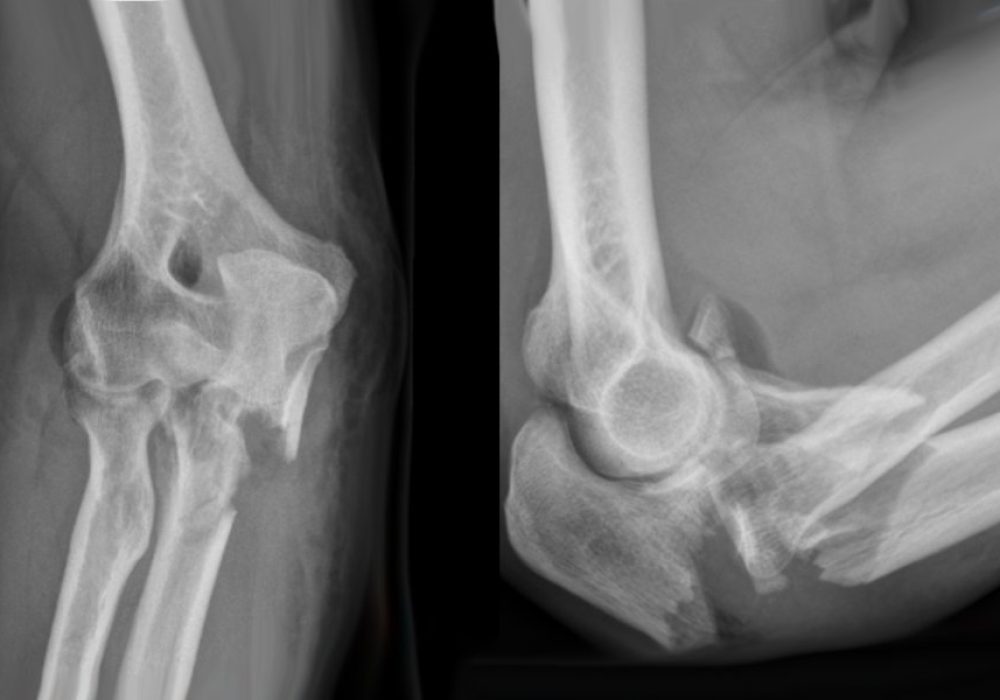
Complex Elbow Fracture Fixation: Causes, Diagnosis, Surgical Treatment, and Recovery
Elbow fractures are injuries involving one or more bones of the elbow joint, including the distal humerus, proximal radius, and ulna. Complex elbow fractures are severe injuries that often involve multiple fracture fragments, joint dislocation, and soft tissue damage. These fractures require meticulous surgical fixation to restore joint stability, function, and prevent long-term complications such as stiffness and arthritis.
Understanding Complex Elbow Fractures
The elbow is a hinge joint formed by the articulation of three bones:
- Distal Humerus: The lower end of the upper arm bone.
- Proximal Radius: The upper part of the forearm bone on the thumb side.
- Proximal Ulna: The upper part of the forearm bone on the little finger side.
Complex fractures may involve:
- Comminuted fractures (bone broken into multiple pieces)
- Intra-articular fractures (involving the joint surface)
- Fracture-dislocations (fracture combined with joint dislocation)
- Associated ligament and soft tissue injuries
Causes of Complex Elbow Fractures
- High-energy trauma such as motor vehicle accidents or falls from height
- Sports injuries involving direct impact or twisting forces
- Osteoporotic bone fractures in elderly patients
- Pathological fractures due to tumors or infections
Symptoms
- Severe pain and swelling around the elbow
- Visible deformity or abnormal positioning
- Inability to move the elbow or bear weight
- Bruising and tenderness
- Numbness or tingling if nerves are involved
Diagnosis
1. Clinical Examination
Assessment of swelling, deformity, neurovascular status, and range of motion.
2. Imaging Studies
- X-rays: Anteroposterior (AP), lateral, and oblique views to evaluate fracture pattern.
- CT Scan: Provides detailed 3D images for complex fractures and preoperative planning.
- MRI: Useful for assessing soft tissue and ligament injuries.
Treatment Overview
Complex elbow fractures typically require surgical fixation to:
- Restore bone alignment and joint congruity
- Stabilize the fracture fragments
- Allow early mobilization to prevent stiffness
Surgical Fixation Techniques
1. Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF)
ORIF is the standard surgical approach for complex elbow fractures. It involves:
- Making an incision to expose the fracture site
- Realigning (reducing) the bone fragments anatomically
- Fixing the fragments with plates, screws, or wires
2. External Fixation
Used in cases with severe soft tissue injury or infection risk, external fixators stabilize the elbow externally while allowing soft tissue healing.
3. Total Elbow Arthroplasty
In elderly patients with severely comminuted fractures and poor bone quality, elbow replacement surgery may be considered.
Surgical Procedure
- Anesthesia: General or regional anesthesia.
- Positioning: Patient positioned supine or lateral decubitus with arm supported.
- Approach: Various surgical approaches (posterior, lateral, medial) depending on fracture location.
- Fracture Reduction: Careful realignment of bone fragments.
- Fixation: Application of hardware to secure fragments.
- Soft Tissue Repair: Repair of ligaments and muscles if needed.
- Closure: Layered closure of soft tissues and skin.
Postoperative Care
- Immobilization: Brief period of splinting or bracing.
- Pain Management: Analgesics and anti-inflammatory medications.
- Physical Therapy: Early controlled range-of-motion exercises to prevent stiffness.
- Follow-Up: Regular clinical and radiological evaluation to monitor healing.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
- Gradual increase in elbow movement and strengthening exercises.
- Avoidance of heavy lifting or strenuous activities initially.
- Full recovery may take several months.
- Compliance with rehabilitation is crucial for optimal functional outcome.
Complications
- Elbow stiffness and loss of motion
- Nonunion or malunion of fractures
- Post-traumatic arthritis
- Nerve injury (e.g., ulnar nerve palsy)
- Infection
- Hardware irritation or failure
Prognosis
With timely and appropriate surgical management, many patients regain good elbow function. However, complex fractures carry a higher risk of complications and prolonged recovery compared to simple fractures.
When to See a Doctor
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Severe elbow pain after trauma
- Visible deformity or inability to move the elbow
- Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the hand or arm
- Signs of infection after surgery such as redness, swelling, or fever
Conclusion
Complex elbow fracture fixation is a challenging but essential procedure to restore elbow anatomy and function after severe injuries. Advances in surgical techniques and rehabilitation have improved outcomes, but early diagnosis, expert surgical care, and dedicated rehabilitation remain key to successful recovery. If you have sustained a complex elbow fracture, consult an orthopedic specialist promptly to discuss the best treatment options.
