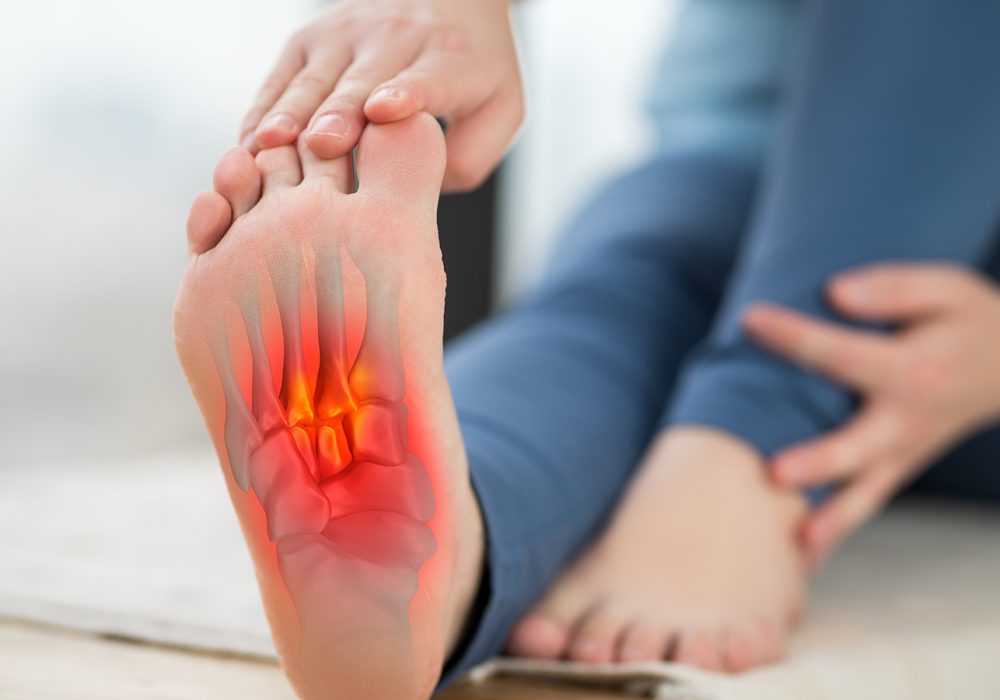
Plantar Fasciitis: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Plantar fasciitis is one of the most common causes of heel pain, affecting millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that runs along the bottom of the foot connecting the heel bone to the toes, becomes inflamed or irritated. This condition can cause significant discomfort and impact daily activities such as walking, running, and standing. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for plantar fasciitis is essential for effective management and recovery.
Foot & Ankle Surgery
Make Your Appointment
What Is Plantar Fasciitis?
The plantar fascia is a fibrous connective tissue that supports the arch of the foot and absorbs shock during movement. Plantar fasciitis develops when this tissue is overstretched or overused, leading to microtears, inflammation, and pain, particularly near the heel.
Causes of Plantar Fasciitis
Several factors can contribute to the development of plantar fasciitis, including:
1. Overuse and Repetitive Stress
Activities that place excessive stress on the plantar fascia, such as running, jumping, or prolonged standing, can cause irritation and inflammation.
2. Foot Mechanics
Abnormal foot structures or mechanics, such as flat feet, high arches, or an abnormal gait, can increase strain on the plantar fascia.
3. Obesity
Excess body weight increases pressure on the plantar fascia, contributing to inflammation.
4. Age
Plantar fasciitis is most common in people between 40 and 60 years old, as the plantar fascia loses elasticity with age.
5. Improper Footwear
Wearing shoes with poor arch support, inadequate cushioning, or worn-out soles can exacerbate plantar fascia stress.
6. Occupation
Jobs that require long hours of standing or walking on hard surfaces increase the risk.
Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis
- Sharp, stabbing pain near the heel, especially with the first steps in the morning or after periods of rest
- Pain that worsens with prolonged standing, walking, or activity
- Tenderness and swelling at the bottom of the heel
- Stiffness in the foot and difficulty flexing the foot upward
Diagnosis
1. Medical History and Physical Examination
The doctor will inquire about symptoms, activity levels, and footwear habits. Physical examination focuses on identifying tenderness along the plantar fascia and assessing foot mechanics.
2. Imaging Studies
- X-rays: To rule out other causes of heel pain such as fractures or bone spurs.
- Ultrasound or MRI: May be used to assess the plantar fascia thickness and inflammation in chronic or unclear cases.
Treatment Options
Most cases of plantar fasciitis improve with conservative treatment. The goals are to reduce pain, decrease inflammation, and promote healing.
Non-Surgical Treatments
- Rest and Activity Modification: Avoid activities that exacerbate pain.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice to the heel to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Stretching Exercises: Targeting the plantar fascia, Achilles tendon, and calf muscles to improve flexibility.
- Footwear Modifications: Wearing supportive shoes with good arch support and cushioning.
- Orthotic Devices: Custom or over-the-counter shoe inserts to support the arch and reduce strain.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to relieve pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Techniques such as massage, ultrasound therapy, and strengthening exercises.
- Night Splints: Devices that keep the foot in a dorsiflexed position overnight to stretch the plantar fascia.
Surgical Treatments
Surgery is rarely needed and considered only after 6 to 12 months of unsuccessful conservative treatment. Options include:
- Plantar Fascia Release: Partial cutting of the plantar fascia to relieve tension.
- Removal of Bone Spurs: If present and causing symptoms.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Recovery involves gradual return to activity with continued stretching and strengthening exercises. Maintaining a healthy weight and wearing appropriate footwear are important to prevent recurrence.
Prevention
- Wear supportive shoes with proper arch support and cushioning.
- Avoid walking barefoot on hard surfaces.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Incorporate stretching exercises for the feet and calves into your routine.
- Gradually increase activity intensity to avoid overuse.
- Use orthotic devices if recommended.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical advice if you experience:
- Persistent heel pain lasting more than a few weeks
- Severe pain that limits daily activities
- Swelling, redness, or warmth around the heel
- Numbness or tingling in the foot
Conclusion
Plantar fasciitis is a common and often painful condition that can significantly affect mobility and quality of life. With early diagnosis and appropriate treatment, most individuals recover fully. Preventive measures and lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing symptoms and avoiding recurrence. If you experience heel pain consistent with plantar fasciitis, consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan.
